Understanding Different Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a surprisingly common condition that affects people of all ages. It can range from mild to profound, impacting daily life in various ways. If you suspect you or someone you know might have hearing loss, understanding the different types can be the first step toward finding solutions.
Let’s understand the different types and their causes, which will help you seek a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves cannot travel freely through the outer or middle ear. This can happen for several reasons:
● Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal, thus hindering sound transmission.
● Ear Infections: Middle ear infections, especially when frequent or fluid-filled (otitis media with effusion), can temporarily dampen hearing.
● Ruptured Eardrum: An eardrum tear disrupts the middle ear's normal functioning, leading to conductive hearing loss.
● Foreign Objects: Objects lodged in the ear canal can obstruct sound waves.
The symptoms of this hearing loss typically involve difficulty hearing faint sounds and muffled speech. In some cases, you might experience a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. The good news is that conductive hearing loss is often treatable. Treatment can involve removing earwax, antibiotics for infections, surgery for a ruptured eardrum, or removing any foreign objects.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
This type is a more permanent form of hearing loss that arises when the inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged. The inner ear houses the cochlea, a snail-shaped organ containing hair cells that convert sound waves into electrical signals the brain interprets as sound. Damage to these hair cells or the auditory nerve disrupts this process, leading to hearing loss.
Causes of sensorineural hearing loss include the following:
● Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis): This is the most common type of sensorineural hearing loss, which gradually develops with age.
● Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Exposure to loud noises over time can damage hair cells in the inner ear. Working in noisy environments or prolonged use of headphones at high volumes can cause sensorineural hearing loss.
● Ototoxic Medications: Certain medications can have ototoxic side effects, meaning they can damage the inner ear and cause hearing loss.
● Head Injuries: Trauma to the head can sometimes injure the inner ear or auditory nerve, leading to hearing loss.
● Meniere's Disease: This inner ear disorder causes symptoms like vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and fluctuating hearing loss.
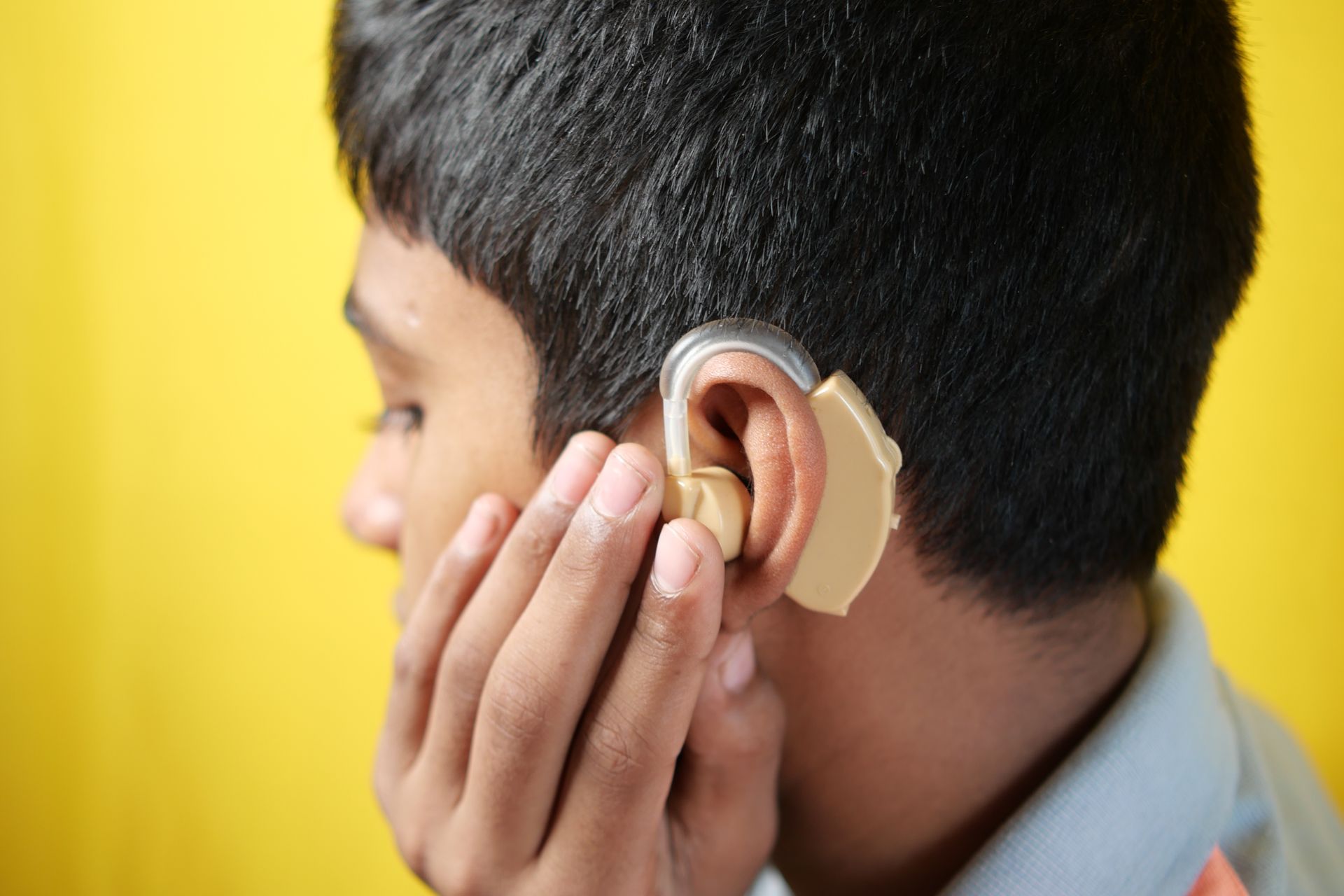
Sensorineural hearing loss can manifest in various ways, including difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds, problems understanding speech in noisy environments, and muffled or distorted sounds. Unfortunately, there's no cure for this hearing loss, but there are ways to manage it effectively. Hearing aids can significantly amplify sounds, improving hearing ability. Cochlear implants might sometimes be an option for severe hearing loss.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss occurs when someone experiences both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss simultaneously. This can happen due to a combination of factors affecting both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear. For instance, someone with chronic ear infections (conductive) might also have age-related hearing loss (sensorineural).
The symptoms and treatment for mixed hearing loss depend on the underlying causes. Typically, a combination of treatments addressing conductive and sensorineural components might be recommended.
Do you suspect hearing loss? Don't wait! At ENT Medical and Surgical Group, our experienced team can diagnose your hearing concerns, treat sinus issues, and provide solutions for allergies. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and rediscover the joy of clear sound.